SkillPilot Whitepaper (EN)
Version: 1.0.15 Date: February 2026 Project: SkillPilot
Summary
SkillPilot connects to existing curricula and uses them as the source of truth (e.g., state curricula, module handbooks, standards like CEFR). SkillPilot does not replace these standards; it translates them into a machine-readable skill graph. Learners, teachers, and an AI tutor use this as a machine-readable map. This allows the learner to move safely from their current skill state to their skill goals. The AI tutor leads the dialogue – relying on the exact backend logic for learning status, rules, and next steps.
To achieve this, the system records learning achievements on atomic skill goals and derives the mastery level for higher-level topics. On this basis, the path via the next attainable skill goals leads systematically to individual educational objectives.
Quality assurance is anchored in a practice-driven Champion program and the open-source workflow (Issues/PRs).

1. The Challenge: Individual Skill Navigation Does Not Scale
Education follows curricula that are defined by the state or through accreditation. In practice, there is a gap between curriculum and learning reality:
- Learners do not start at the same point (prior knowledge, pace, gaps).
- Teachers still have to guide many people in parallel, often in large cohorts.
- Learning goals usually exist as text, but not as a navigable structure with dependencies and sensible next steps.
This leads to overload for some, boredom for others, and high effort to track learning states and next steps.
SkillPilot closes this tool gap: outcome-oriented navigation in the curriculum without turning teachers into "bookkeepers." SkillPilot builds on the existing curriculum - it does not create new standards, it makes existing standards operational and navigable.
2. The Shift: Why Hybrid AI Systems Are the Right Approach
In the three years since ChatGPT went online in November 2022, the world of language-based AI has developed rapidly. A sense of this pace is provided by a look at Humanity's Last Exam, the toughest AI benchmark to date. Introduced in early 2025 to test KIs with thousands of extreme expert questions for true logical reasoning rather than mere knowledge, leading models were still failing almost completely at the beginning of the year (under 10% success), but were able to quintuple this performance to about 50% by year-end.
As of late 2025, KIs are thus professionally and linguistically up to many topics taught at schools and universities. But they have limits: They are not trained pedagogues and do not work like algorithmically exact bookkeeping programs that calculate and manage without error.
To ensure the algorithmic precision required for SkillPilot in navigating learning goals, another trend benefits us: Coupling language KIs to classical software. Standards are being established that allow KIs like ChatGPT to specifically call interfaces (APIs) of classical programs.
The approach for SkillPilot follows almost automatically: It emerges as a hybrid application. Classical, exact software handles the precise "bookkeeping" and navigation of skill goals in the background. Leading language KIs are instructed (as SkillPilot GPT) to speak with learners as empathetic trainers, but use the software's exact logic in the background for learning progress.
3. The Product: How SkillPilot Works
3.1 The Technology: The Skill Graph (Source of Truth & Frontier)
SkillPilot replaces linear lists with a connected graph.

Plugging into Existing Curricula (Raw Input & Traceability)
SkillPilot does not "invent" curricula: curricula, module handbooks, or standards serve as raw input and are translated into a skill graph.
The integrity of the graph is ensured by a formal mathematical specification (Acyclicity, Effective Requires, Transitive Minimality), which prevents circular references and logically validates dependencies.
This is about:
- Operationalization: learning outcomes are broken down into atomic skill goals (without changing the standard).
- Traceability: each skill remains traceable to source/section/version.
- Navigability: prerequisites and hierarchies are modeled explicitly so paths are plannable (didactic prereqs possibly as overlays). The graph does not enforce rigid paths: It supports pedagogical flexibility. The Optimistic Mode checks prerequisites only within the selected filter (e.g., grade level), allowing learners to enter directly in the target year without blocking due to gaps from earlier years. When learners struggle, the tutor switches to diagnostic Pessimistic Mode to identify the missing foundation.
- Governance: changes currently run via GitHub (Issues/PRs), versioning via GitHub history (see section 6).
Map: Nodes & Edges
- Nodes: atomic skills ("can explain/apply X") and atomic clusters (topics/modules).
- Edges:
- Prerequisites: "A before B"
- Contains/Part-of: "X includes Y and Z"
Three Node Types in Practice
SkillPilot distinguishes three node types that reflect different learning modes:
- Tutorial: All subject topics are explained and practiced with the AI tutor.
- Memorize: Individual facts are memorized (flashcards/SRS).
- Exam: Abitur-style tasks are solved independently (e.g., photo from notebook/paper), immediately graded (points, pass/fail, errors), and then explained.
In the curriculum Upper Secondary School (DE, HE, G9, Secondary II) – Mathematics (QA Stage 2), all three node types are used.

Formal specification: The mathematical definition of the graph (e.g., acyclicity, Effective Requires) is publicly documented:
Graph definition
Frontier: Next Reachable Steps
SkillPilot computes the frontier: skills whose prerequisites are met but not yet mastered.
This avoids jumps and keeps learning in the zone of sensible next steps. We call this boundary of current knowledge the Frontier (didactically: Zone of Proximal Development according to Vygotsky). It marks exactly the skills that are learnable next.
The frontier is not an AI recommendation, but the mathematically computed set of all logically unlocked learning goals.

3.2 The Interaction Layer: The AI Tutor
The skill graph provides the route, but learners do not interact with datasets; they need a guide. This role is taken by the AI Tutor (SkillPilot GPT). It serves as an intuitive interface that translates the abstract instructions of the graph into natural, motivating language.
The tutor is not a "black box" but acts strictly based on backend logic: it receives the next goal and allowed transitions from the graph, illustrating them in a didactically meaningful dialogue. This turns "exact bookkeeping" into a personal learning experience.
3.3 The Hybrid Learning Loop: Understanding + Memorizing + Practice
The Frontier calculated in Chapter 3.1 serves as a focus filter for the tutor: from the total set, only the content that fits the goal and current state is shown - the next feasible step instead of "everything at once".
Mastery: Progress as an Evidence Model

Mastery is not a logbook but a derived status from learning interactions. For interoperability, a simple evidence model helps:
- Formative: tutor dialogs, in-chat tasks, quick checks.
- Optional stronger: quizzes, task series, artifacts (solution steps/code/short text), oral checks.
- Optional review: skills can later require a re-check.
SkillPilot makes progress visible - the institution decides which evidence has which consequences.
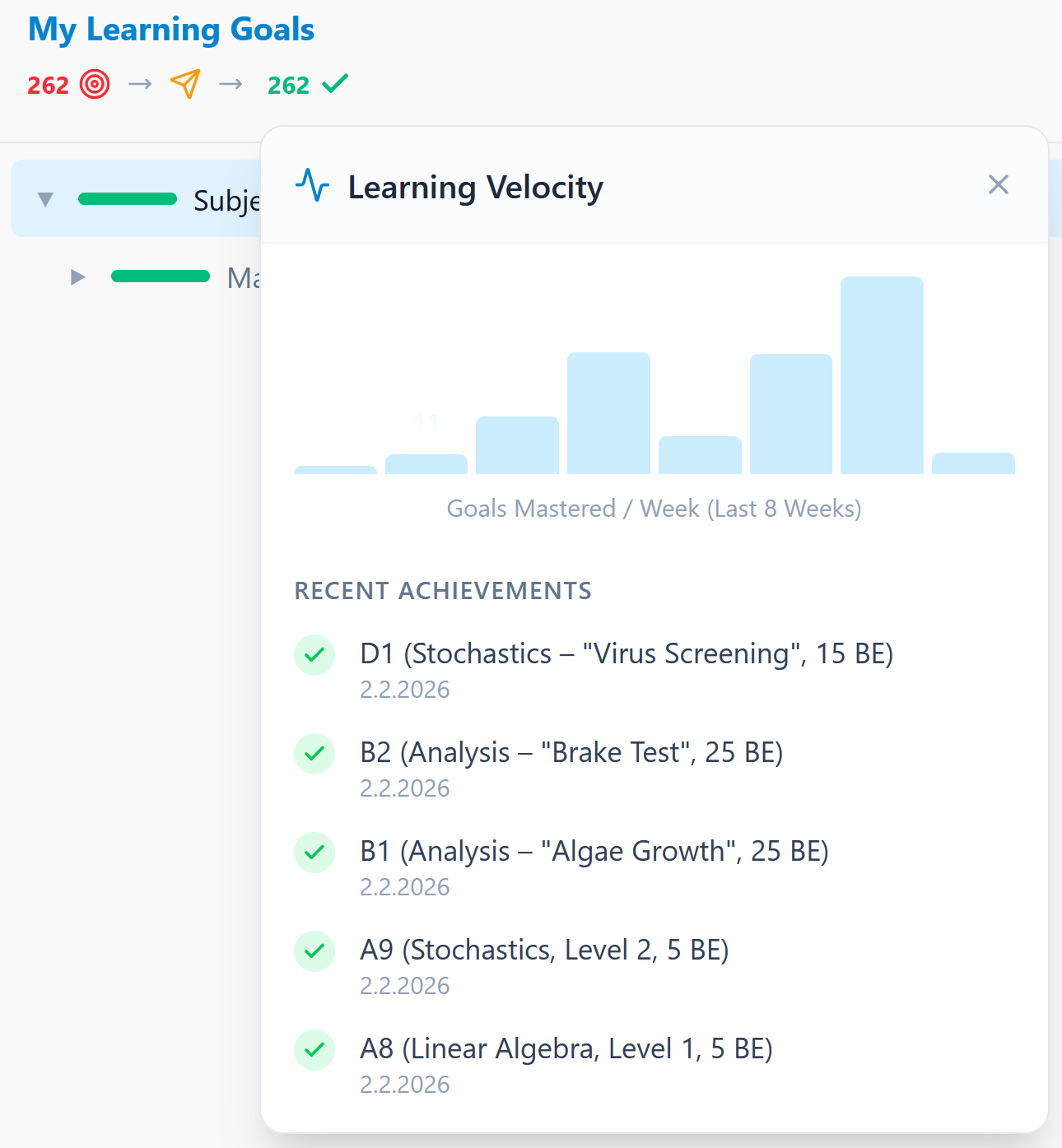
Learning Velocity
Learning velocity shows how many atomic goals are newly mastered per week - a simple indicator of rhythm and continuity.
3.3 The Hybrid Learning Loop: Understanding + Memorizing + Practice
Not every learning goal is learned the same way: concepts need understanding and application, facts need repetition - and many skills need active doing (e.g., programming, calculating, writing).
The skill graph models understanding and dependencies. For pure memorization (vocabulary, formulas, facts), spaced repetition is more efficient.
SkillPilot integrates a flashcard drill engine (SRS):
- Competence loop: the skill graph defines what comes next.
- Memorization loop: the drill engine optimizes how to repeat (intervals, prioritization; e.g., SuperMemo-2).
In addition, other learning modes are needed for "doing" skills: the tutor should send learners into suitable practice formats (e.g., problem sets, programming tasks, writing/speaking exercises) and then guide them back in chat for evaluation, feedback, and transfer.
4. Trust Architecture: Security & Integrity
4.1 Data Approach: Security & Privacy by Design
A central pillar of SkillPilot is data separation.

Pseudonym Instead of Identity
The SkillPilot server knows learners only as a pseudonym (skillpilotId).
On the server, only technically necessary metadata are stored, e.g., learning progress in the graph.
Dialog Content Is Decoupled
The dialog content (tutor conversations) is decoupled from the SkillPilot server, keeping the central data store minimal.
Recommendation for educational institutions:
Clear guidelines on which data should not be shared in tutor chats (sensitive personal data) and how learners are supported safely.
Mapping Inside the Institution (Local)
The mapping "who is which pseudonym?" stays with the institution/teacher and is stored locally (e.g., in protected storage) - not centrally.
AI Frontend / Provider Choice (Sovereignty)
The tutor dialog happens in the respective AI frontend (currently: ChatGPT as the reference integration) and is subject to its operational and privacy framework.
For contexts with higher sovereignty requirements, alternative AI backends up to local models are planned. They must reliably meet the required properties (tool use, stability, structure, didactics).
4.2 Chain of Custody: Integrity & Traceability
To keep learning states portable and verifiable, SkillPilot uses a chain-of-custody pattern.
- Tutor instances authenticate to the backend.
- Write access for progress updates is granted only to authorized actors (current pattern: the tutor as the writing actor).
Signed Exports
Learners can export profile + progress.
The server cryptographically signs these exports so offline manipulation is detectable.
Data Provenance on Import
On import (e.g., transfer, backup), the full provenance chain can be carried along. This makes it visible whether a state was continued or taken from elsewhere.
Important: Chain of custody protects integrity and provenance - it is a transparency tool, not a complete fraud-prevention system.
5. The Ecosystem: Content & Standards
5.1 Status Quo: Available Content (Examples)

SkillPilot is not just a concept: it already contains curricula/standards as starting points. The key is the quality stage:
- Stage 1 – AI-derived draft
Learning goals in SkillPilot are derived from publicly accessible, official curricula/regulations. We cite the sources; SkillPilot provides its own structuring and summary – not official wording.
Outcome: The curriculum exists and is visible in the UI. - Stage 2 – QA by Curriculum Champion
A Curriculum Champion has mastered a curriculum or a module inside SkillPilot, cleaned errors in the curriculum and SkillPilot, and awarded a QA checkmark. A curriculum can collect multiple QA checkmarks.
Current status: The subject Mathematics for Gymnasiale Oberstufe (DE, HE, G9, Secondary II) has now reached Stage 2. All other curricula are currently in Stage 1. The current status is visible in the Curriculum Directory.

Curriculum Champions (practice anchor):

Champions take responsibility for a curriculum or a clearly scoped topic area*.
* They work through the curriculum, gather practice feedback, and channel it into Issues/PRs.
* Visibility creates accountability: Champion profiles show engagement (e.g., Issues/PRs) and progress.
The QA process does not only cover curricula: the SkillPilot AI tutor is continuously qualified in real-world use so that the experience remains reliable and didactically sound across curricula.
Schools (Bavaria & Hesse, Germany)
Bavaria: * Grundschule (Primary School, complete: Grades 1–4) * Mittelschule (Middle School, complete: Grades 5–10) * Realschule (Secondary School, complete: Grades 5–10) * Gymnasium (Academic High School, complete: Grades 5–13) * Fachoberschule & Berufsoberschule (Vocational High School) * Wirtschaftsschule (Business School)
Hesse: * Gymnasiale Oberstufe (G9, Secondary II) * Gymnasiale Mittelstufe (G9, Secondary I)
Higher Education (Bologna-relevant)
- Uni Heidelberg: Bachelor Biosciences, Master Molecular BioSciences, Physikum (Medicine)
- Uni Mannheim: Bachelor Business Administration (BWL), Bachelor Law, Master Law
- TU Darmstadt: Bachelor Computer Science
- TU Munich: Bachelor Computer Science (Informatics), Bachelor Mathematics, Bachelor Physics, Master Quantum Science and Technology, Master Theoretical and Mathematical Physics, Executive Master of Business Administration (MBA)
Languages (CEFR A1-C2)
- English (A1-C2)
- French (A1-C2)
The listed curricula are currently in Stage 1 (AI-derived). The process to move them to Stage 2 runs via the Curriculum Champion process.
[!IMPORTANT] We invite you to actively shape this process: Become a Curriculum Champion and help ensure the quality and practical relevance of your subject area.
The content is extensible and versioned; source references are documented, and changes currently flow through GitHub (Issues/PRs).
5.2 SkillPilot in the Bologna/EHEA Context (Short Overview)
Bologna/EHEA sets the framework for outcomes, transparency, recognition, and quality in higher education. SkillPilot can support these goals, but it does not replace institutional decisions.
- Learning outcomes / competencies: Contribution: Make outcomes navigable as a skill graph; progress visible. Limit/prerequisite: Clean modeling, source references, versioning.
- Credits/workload (ECTS logic): Contribution: Support paths/prereqs and workload transparency. Limit/prerequisite: No credit awarding; rules remain institutional.
- Recognition/mobility: Contribution: Evidence + signed exports as preparation/support. As described in Chapter 4.2, the signed exports provide the technical basis (evidence) to transfer informal learning into formal recognition processes. Limit/prerequisite: Recognition remains a formal process.
- Quality assurance: Contribution: Signals about hurdles/paths for curriculum development. Limit/prerequisite: QA processes + transparent AI rules required.
6. Governance & Community: Open Source & Invitation
SkillPilot is released as open source under the Apache-2.0 license - an invitation to include established stakeholders rather than displace them:
- Institutions retain sovereignty over curricula and content.
- Coupling content to skill goals is possible in the future.
- Open interfaces enable contributions and integration.
Governance & quality assurance (currently via GitHub + Champion program): * Feedback flows through GitHub Issues, often initiated by champions. * Changes to the curriculum/graph run through pull requests (review on GitHub). * Versioning follows GitHub history; curriculum sources are referenced. * More advanced governance mechanisms (e.g., expert review boards, QA processes, overlays) are possible in the future.
Initiator:
The legal entity behind SkillPilot is enpasos GmbH. We invite partners to develop SkillPilot further together - in content, didactics, and technology.
Start your pilot immediately and without registration (ID-based): A guide for the 5-minute start can be found in the Quickstart.
Note: Your ID is the only key to your data - store it safely.
More transparency:
GitHub
Documentation
Graph definition